|
The Quixote system is an artificial intelligence technique for teaching robots and artificial virtual agents how to do things by telling them stories. Stories present a natural means of communicating complicated, tacit procedural knowledge. Quixote thus reads in natural language stories and learns to emulate the behaviors of the characters in the stories. The long term goal of the project is to make AI programming accessible to non-programmers and non-AI experts. We have also shown that stories can be an effective means of demonstrating ethical behavior to robots and AIs.  |
We conduct 3 in-lab and one crowd-sourced experiment in the domains of politics and movies. We find mixed results that interaction traces (visual scents of historical interactions) can increase awareness of bias and impact interactive behavior and decision making.  |
Why is it so hard for chatbots to talk about race? This work explores how the biased contents of databases, the syntactic focus of natural language processing, and the opaque nature of deep learning algorithms cause chatbots difficulty in handling race-talk. In each of these areas, the tensions between race and chatbots create new opportunities for people and machines. By making the abstract and disparate qualities of this problem space tangible, we can develop chatbots that are more capable of handling race-talk in its many forms. |
There are hundreds and thousands of professional conferences across the globe. While a lot of people come to seek new insights, learn and present, a huge chunk of people also look for networking opportunities with other attendees. However, initial discoveries were made that actually, there are some gaps in how attendees network with others especially before and after the conferences.  |
|
Business analysts create logomaps in order to better understand and communicate trends in the world of business. Humans can intuitively make sense of these maps, while computers struggle to extract the same knowledge. Using computer vision and human-in-the-loop machine learning, this research aims to create tools and methods for automating knowledge extraction from graphical logomaps.  |
Lonely Mountain is a virtual reality adaptation of the movie The Hobbit: The Battle of the Five Armies. In this VR experience, Lonely Mountain has fallen into the claws of Smaug the Terrible. You will take the role of the Hobbit, Bilbo Baggins. Your mission is to find and recover the Arkenstone, and unite the dwarf realms once more under the same banner to save Lonley Mountain. The scenario has Bilbo reaches the treasure room and picks up a tool to grab the Arkenstone from the claws of Smaug without waking up Smaug.  |
This research investigated whether providing directional alerts to a user's active screen can augment their ability in regaining situational awareness when traveling in an autonomous vehicle (AV). |
|
|
LuminAI is an interactive art installation that explores the improvisation of proto-narrative movement between humans and virtual AI agents using full body, expressive, movement-based interaction. Interactors can co-create movement with an autonomous virtual agent that learns movement, response, and improvisation directly from interacting with human teachers. It analyses their movement using Viewpoints movement theory. |
Lumos is a visual data analysis tool that captures and shows the interaction history with data to increase awareness of such analytic behaviors. Using in-situ (at the place of interaction) and ex-situ (in an external view) visualization techniques, Lumos provides real-time feedback to users for them to reflect on their activities. For example, Lumos highlights datapoints that have been previously examined in the same visualization (in-situ) and also overlays them on the underlying data distribution (i.e., baseline distribution) in a separate visualization (ex-situ). 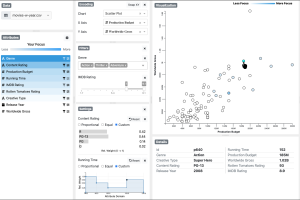 Website: |
Machine Teaching is a collection of approaches explicitly aimed at solving the difficulties that lie in enabling domain experts to effectively teach machine learning systems. AI Systems, including agents like Jill Watson, face significant challenges in adapting to new domains. |
Gestures for interfaces should be short, pleasing, intuitive, and easily recognized by a computer. However, it is a challenge for interface designers to create gestures easily distinguishable from users' normal movements. Our tool MAGIC Summoning addresses this problem. Given a specific platform and task, we gather a large database of unlabeled sensor data captured in the environments in which the system will be used (an "Everyday Gesture Library" or EGL). MAGIC can output synthetic examples of the gesture to train a chosen classifier. 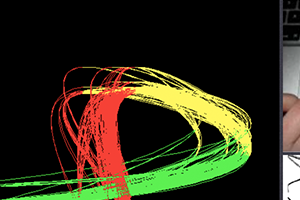 |
|
Magic Window supports immersive augmented video experiences allowing viewers to change perspective, as if they are looking through a real window. A rich set of collaborative interactions with live and pre-recorded media content as well as connected devices are possible through gesture-based controls.  |
The project was inspired by the notion of a temporary, magical social space. It resulted in a tangible interface in the form of an umbrella that reacts to sound, movement, and tactile input. The result is a playful experience with the umbrella that can be shared as participants hide from the rain (thus creating an impromptu social space) and explore their umbrella's "magic" functionality together  |
MagTrack is a wearable alternative controller designed for power wheelchair users with limited upper-body mobility to regain better autonomy of their physical and digital life.  Website: |


