|
The Covid-19 pandemic has certainly caused a lot of disruption in how universities operate. Proactive campuses use a combination of testing, tracing, and encouraging safe practices to contain infectious spread while still maintaining some semblance of operation. In this video, we will present some work on using WiFi authentication logs to support contact tracing (identifying potential contacts) as well as understanding the impact of policy (e.g., online teaching only) on infectious spread. |
Dino-Store is a persuasive game that was designed to use gamification way to communicate with people and raise awareness on COVID-19. The game’s setting is grocery shopping and the mechanic indicates that how different protection strategies, such as wearing mask, keeping social distance can affect people’s infection chances in the COVID-19 pandemic. |
Using a sample of 32 million Reddit posts, we characterize the removal explanations that are provided to Redditors, and link them to measures of subsequent user behaviors—including future post submissions and future post removals. |
|
|
“Don't Open That Door” is a gesture-based interactive narrative project set in the universe of the TV show Supernatural. This project creates a dramatic agency for the interactor by leveraging expectations of the horror genre within a seamless scenario that elicits expressive actions and provides a dramatically satisfying response. We match interaction and narrative elements to support the following design goals: Story-driven Physical Reactions, Persistent and Uninterrupted Narrative, Scripting of the Interactor by Narrative.  |
Business ecosystems are characterized by large, complex, and global networks of firms, often from many different market segments, all collaborating, partnering, and competing to create and deliver new products and services. Given the rapidly increasing scale, complexity, and rate of change of business ecosystems, as well as economic and competitive pressures, analysts are faced with the formidable task of quickly understanding the fundamental characteristics of these interfirm networks. 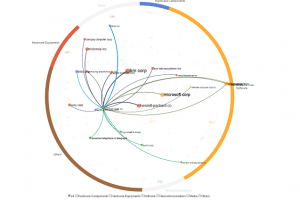 |
A multi-agent AI that incorporates elements of the human visual perception theory and is capable of co-creating non-representational art with a human collaborator on the web. 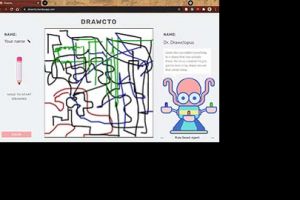 |
|
|
Collaboration is known to push creative boundaries and help individuals sustain creative engagement, explore a more diverse conceptual space, and synthesize new ideas. While the benefits of human collaboration may seem obvious, the cognitive mechanism and processes involved in open-ended improvisational collaboration are active areas of research. Our research group has developed a co-creative drawing partner called the Drawing Apprentice to investigate creative collaboration in the domain of abstract drawing. 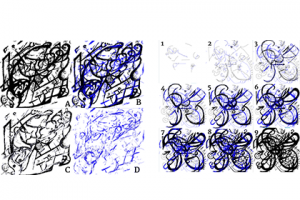 |
We propose a general framework for character self-dressing interactions with simulated clothing. We show that by breaking the process of dressing into sub goals, we can design specific action controllers which, when combined allow a character to put on a garment via a user defined style. 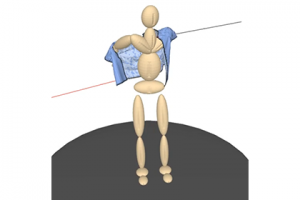 |
Applying driving simulators for in-vehicle research allows for a wide range of studies to be performed particularly when investigating cognitive demand and distraction caused by devices in the car. By using simulations, researchers can investigate driving behaviors in high-risk situations without putting participants or others in harm's way. Currently being conducted within the School of Psychology at Georgia Tech, in-vehicle research could provide more insight into behavior and increase in applicability if participants were able to drive in areas that they are familiar with.  |
Investigating the piloting of drones by non-aviation or licence operators. |
|
Designs for Foraging is a design project that explores the use of IoT technologies in support of urban foraging. Through this project, we are developing use-cases; prototyping hardware, software and user interfaces; and exploring the use of open technologies for image capture and analysis. The underlying motivation for this project is to use design as a means of investigating future practices and to provide the basis for near-term open innovation with IoT in support of alternative practices of agriculture.  |
Part of the fun of computer games is to master the skills necessary to complete the game. Challenge tailoring is the problem of matching the difficulty of skill-based events over the course of a game to a specific player's abilities. We have devised a data-driven approach to predict changes in players' skill mastery over time. By modeling players' skill mastery, we are able to dynamically select game content that challenges individual players at the ideal level, avoiding frustration and boredom. 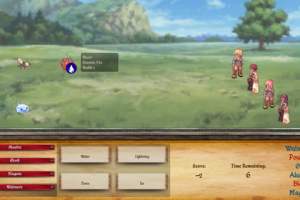 |
We demonstrate a wearable system that detects eating instances in real time. |


